- English
- Español
- Português
- русский
- Français
- 日本語
- Deutsch
- tiếng Việt
- Italiano
- Nederlands
- ภาษาไทย
- Polski
- 한국어
- Svenska
- magyar
- Malay
- বাংলা ভাষার
- Dansk
- Suomi
- हिन्दी
- Pilipino
- Türkçe
- Gaeilge
- العربية
- Indonesia
- Norsk
- تمل
- český
- ελληνικά
- український
- Javanese
- فارسی
- தமிழ்
- తెలుగు
- नेपाली
- Burmese
- български
- ລາວ
- Latine
- Қазақша
- Euskal
- Azərbaycan
- Slovenský jazyk
- Македонски
- Lietuvos
- Eesti Keel
- Română
- Slovenski
- मराठी
- Srpski језик
What Is 2-Thiophene Ethanol ?
2025-09-02
In the field of fine chemicals and advanced organic synthesis, 2-Thiophene Ethanol has become an essential intermediate due to its unique molecular structure and wide applicability across multiple industries. With growing demand for high-purity intermediates, researchers and manufacturers are paying increasing attention to compounds like 2-Thiophene Ethanol, which offer versatility, stability, and efficiency in synthesis.
Understanding 2-Thiophene Ethanol: Structure, Properties, and Specifications
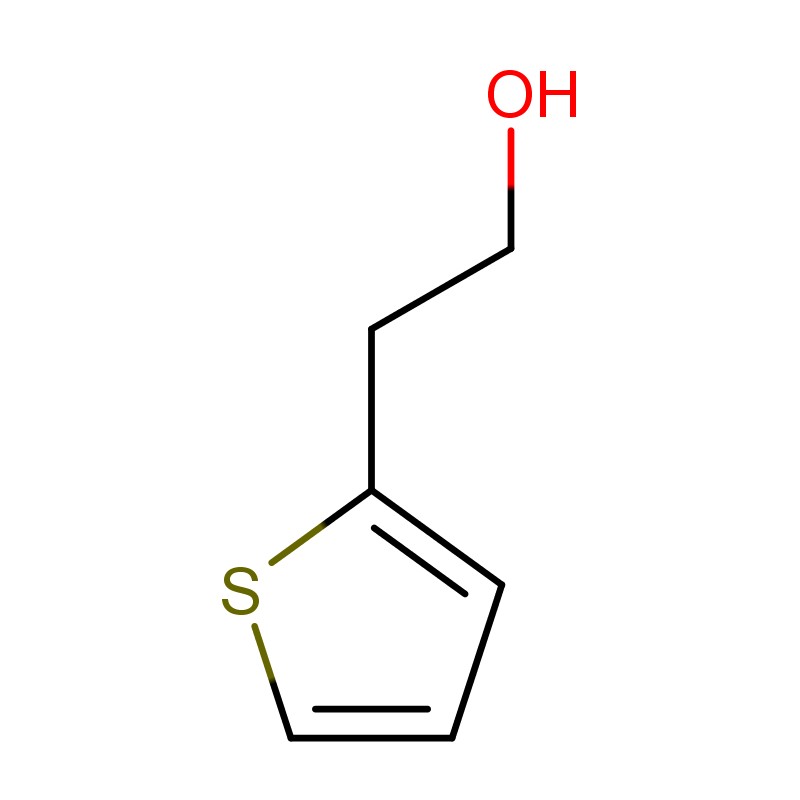
2-Thiophene Ethanol (C₆H₈OS) is an aromatic sulfur-containing compound belonging to the thiophene family. It is characterized by a thiophene ring — a five-membered heterocyclic ring with four carbon atoms and one sulfur atom — attached to an ethanol side chain at the 2-position. This structural configuration grants the molecule both aromatic stability and reactive hydroxyl functionality, making it suitable for use as a versatile synthetic building block.
Key Physical and Chemical Properties
| Property | Specification |
|---|---|
| Chemical Name | 2-Thiophene Ethanol |
| Molecular Formula | C₆H₈OS |
| Molecular Weight | 128.19 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colorless to light yellow liquid |
| Boiling Point | ~220°C |
| Density | ~1.19 g/cm³ |
| Purity | ≥ 99% |
| Solubility | Soluble in alcohols, ethers, and organic solvents |
| Storage Conditions | Store in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area; avoid direct sunlight |
The combination of aromaticity from the thiophene ring and functional versatility from the hydroxyl group makes 2-Thiophene Ethanol highly reactive for coupling reactions, esterification, and alkylation processes.
Industrial Applications of 2-Thiophene Ethanol
2-Thiophene Ethanol is not just a laboratory curiosity; it has become an essential intermediate in various high-value chemical sectors. Below are its primary industrial applications:
A. Pharmaceutical Industry
In pharmaceuticals, 2-Thiophene Ethanol serves as a critical intermediate in the synthesis of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). Its thiophene moiety is commonly used in drug discovery because of its bioisosteric properties — replacing benzene rings in drug molecules to improve metabolic stability, solubility, and binding affinity.
Key pharmaceutical uses include:
-
Development of anti-inflammatory compounds
-
Synthesis of antiviral agents
-
Building blocks for cardiovascular drugs
-
Precursors for central nervous system (CNS) modulators
B. Agrochemical Sector
The molecule is also widely applied in pesticides, herbicides, and fungicides. Its thiophene ring offers enhanced biological activity and environmental stability, making it suitable for next-generation agrochemical formulations.
C. Specialty Materials and Fine Chemicals
2-Thiophene Ethanol is frequently used in developing conductive polymers and photoactive materials due to its sulfur-containing heteroaromatic structure. These materials are increasingly utilized in electronic devices, solar cells, and flexible displays.
D. Research and Development
Academic and industrial R&D labs frequently leverage 2-Thiophene Ethanol as a synthetic scaffold to explore novel compounds. Its flexible chemistry makes it a preferred choice for creating libraries of compounds during early-stage drug discovery and material science experiments.
Advantages of Using High-Purity 2-Thiophene Ethanol
Choosing the right supplier for 2-Thiophene Ethanol is critical, especially when it is used in pharmaceutical or material applications where product quality directly impacts results.
Why High Purity Matters
-
Improved Reaction Yields: Impurities can hinder downstream reactions, reducing efficiency.
-
Enhanced Consistency: Ensures batch-to-batch uniformity for large-scale manufacturing.
-
Regulatory Compliance: High-grade materials meet global quality standards required for pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals.
How It Drives Innovation
With increasing demand for green chemistry solutions and sustainable synthesis routes, 2-Thiophene Ethanol is gaining prominence in eco-friendly reactions. Its compatibility with catalytic hydrogenation and cross-coupling reactions makes it ideal for energy-efficient manufacturing processes.
2-Thiophene Ethanol FAQ: Common Questions Answered
Q1. What is the primary use of 2-Thiophene Ethanol in the pharmaceutical industry?
A: 2-Thiophene Ethanol is primarily used as an intermediate for synthesizing active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). The thiophene moiety often serves as a bioisostere for aromatic compounds, enhancing drug performance, bioavailability, and metabolic stability. Its hydroxyl group enables further chemical modifications to develop compounds targeting various therapeutic areas, including antiviral, anti-inflammatory, and neurological drugs.
Q2. How should 2-Thiophene Ethanol be stored to maintain its stability?
A: Proper storage is essential to preserve the compound’s chemical integrity. It should be stored in tightly sealed containers, in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated environment. Direct sunlight, high humidity, and exposure to oxidizing agents should be avoided, as these conditions may lead to degradation or contamination. For sensitive laboratory applications, refrigeration can further improve shelf-life.
With its unique molecular architecture and exceptional versatility, 2-Thiophene Ethanol continues to drive innovation across pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and specialty materials. Its role as a high-performance intermediate has made it a preferred choice for researchers, manufacturers, and material scientists worldwide.
At Leache, we specialize in providing high-purity 2-Thiophene Ethanol that meets stringent quality standards, ensuring optimal performance for your applications. Whether you’re engaged in large-scale pharmaceutical production, specialty materials research, or advanced chemical synthesis, we deliver consistency, reliability, and technical expertise to support your success.
For more information or to discuss your project requirements, contact us today and discover how Leache can help accelerate your innovation.